Neurological
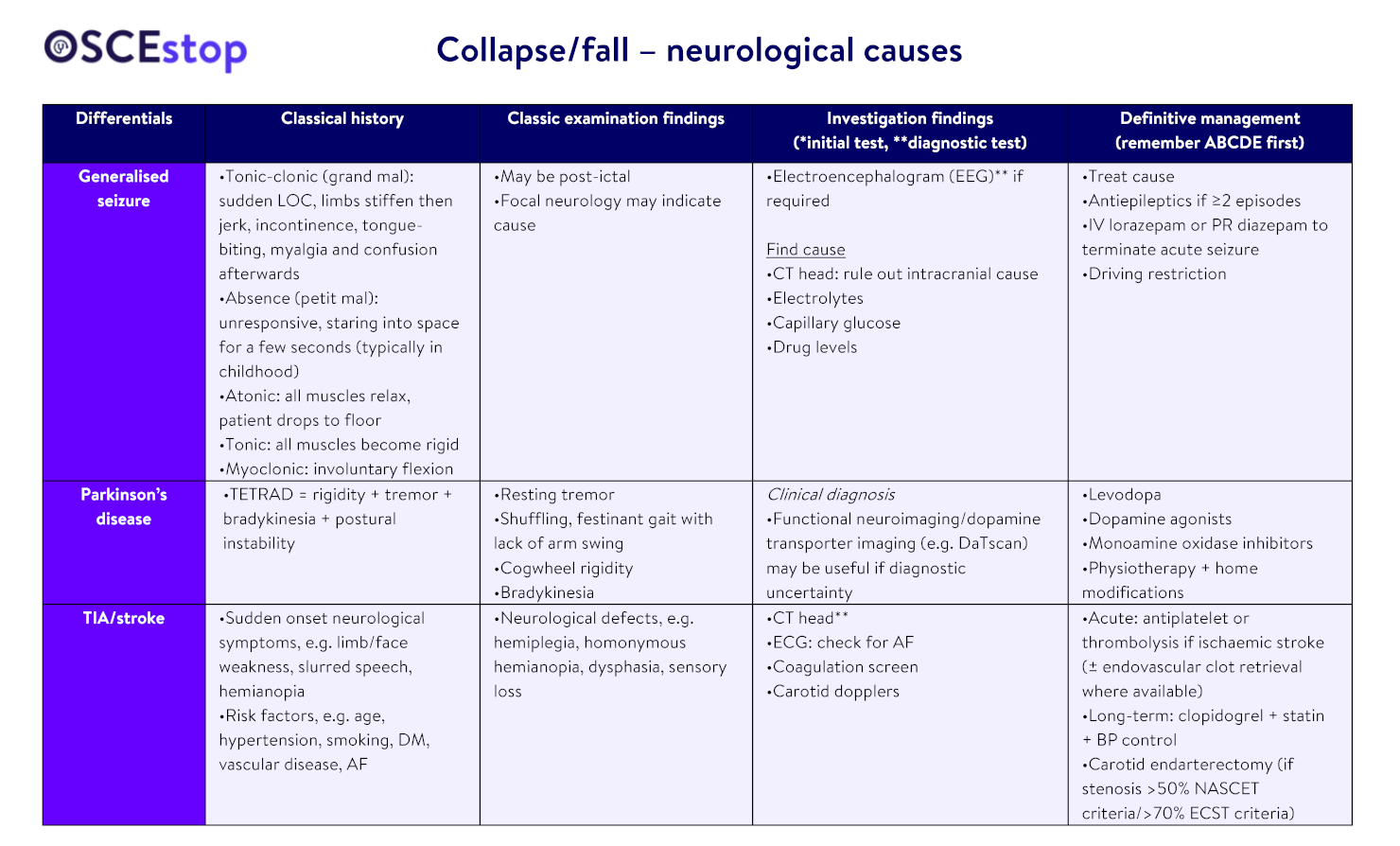
Other neurological differentials = neuropathy (e.g. MS), intracranial haemorrhages (extradural, subarachnoid, subdural), raised intracranial pressure
Cardiovascular
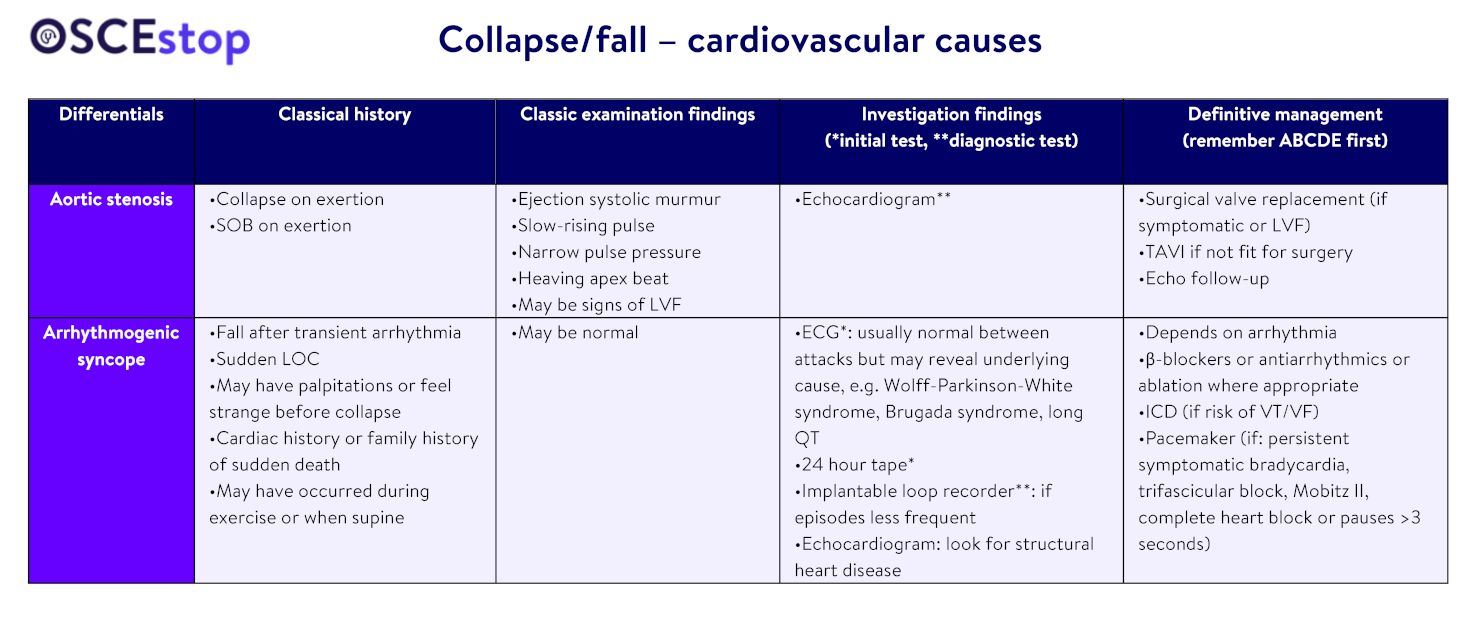
Other cardiovascular differentials
Structural (e.g. hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia)
Massive PE
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency (vertigo precipitated by head extension in elderly patients with cervical osteoarthritis)
Subclavian steal syndrome (proximal subclavian artery stenosis causes retrograde flow in one of the vertebral arteries as they become involved in a collateral circuit to bypass the obstruction)
Reflex
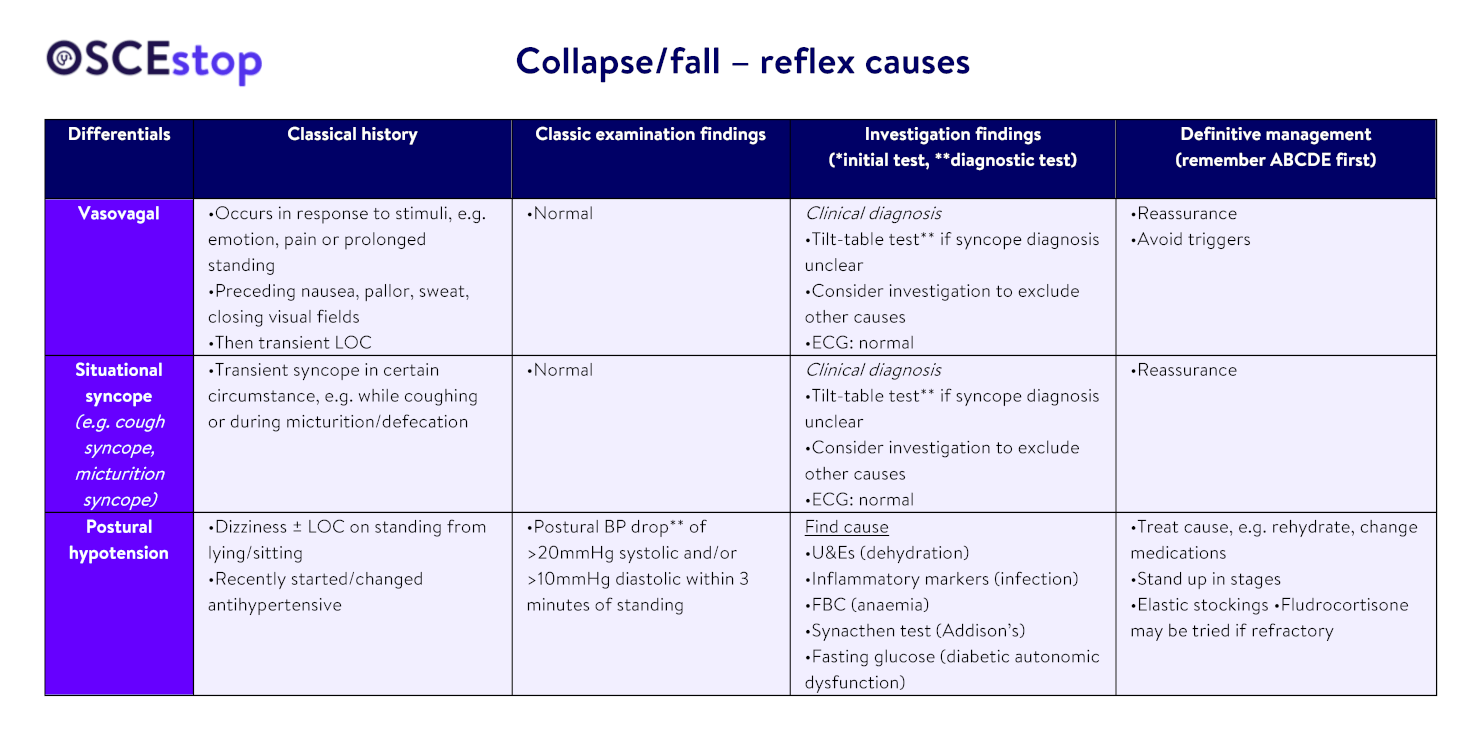
Other reflex differentials
Carotid sinus hypersensitivity (precipitated by head turning/shaving – diagnosed by carotid sinus massage** → ≥3 second pauses)
Other
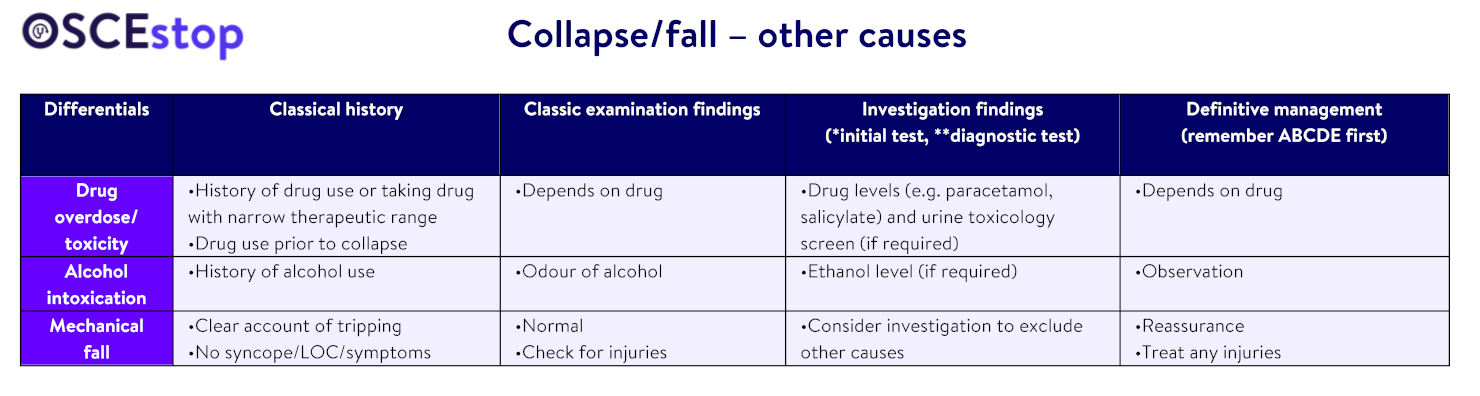
Other differentials = postural instability, polypharmacy, ectopic pregnancy, ruptured AAA, delirium, vertigo, anaemia, hypoglycaemia, hypercapnic acidosis, sepsis, eyesight problems, arthritis, leg weakness, anxiety, factitious blackouts, choking, heat syncope, multifactorial
Test your knowledge
What are the red flag symptoms for cardiac syncope?
Arrhythmogenic:
No warning
Palpitations/feel strange before
Syncope when supine
Chest pain
New/unexplained breathlessness
Cardiac history/severe LVF
Family history of sudden death
Structural (e.g. HOCUM, valve disease):
Syncope on exertion
Cardiac history/lesion
Family history of sudden death
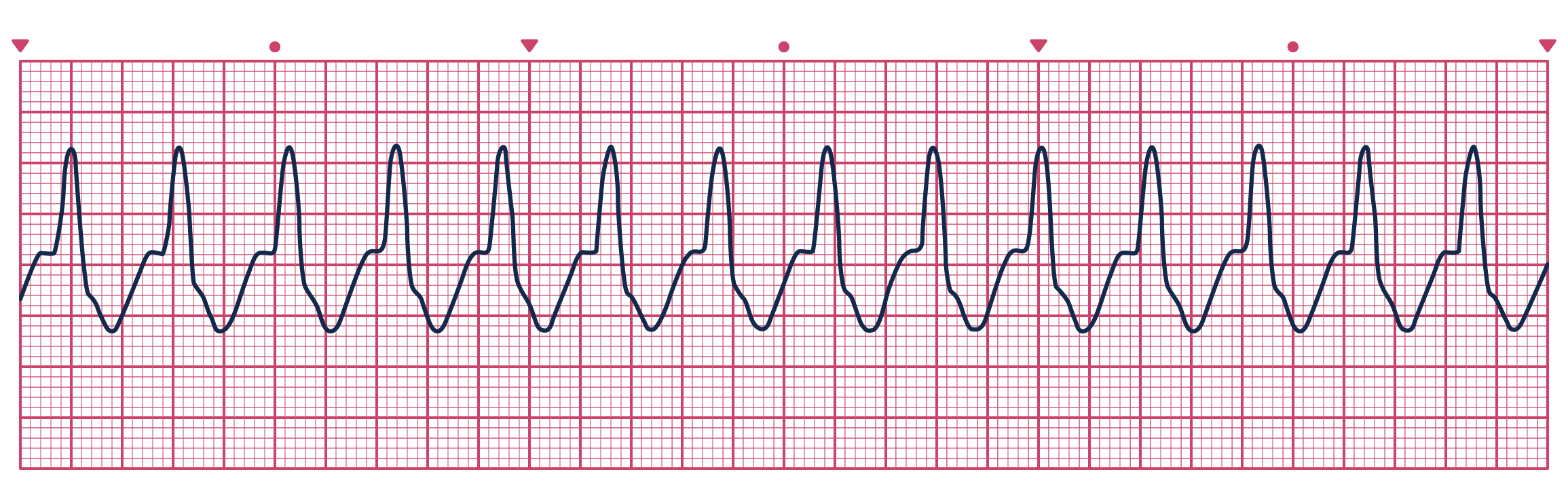
In a patient whom you suspect has cardiac syncope, what would you look for specifically in the ECG?
QT: Long QT or short QT intervalRhythm strip: tachy/bradycardias, pausesPR: heartblock; Delta waves/short PR (WPW)QRS: pathological Q waves (cardiomyopathies); bundle branch block/bifascicular/trifascicular block; ventricular hypertrophy (HOCUM, AS)ST: Brugada pattern (Brugada syndrome); Epsilon waves (AVRD)T: T wave inversion (right leads = AVRD, PE)
What are the different types of generalised seizure?
Absence: brief staring episodeMyoclonic: extremely brief muscle contractions that look like jerky movementsTonic: tense contraction of musclesClonic: rhythmic muscle contractionsTonic-clonic: initial muscle contraction (tonic phase) followed by rhythmic muscle contractions (clonic phase)Atonic: loss of muscle tone
Try some OSCE stations
Status Epilepticus Transient ischemic attack Stroke Find lots more here!